
Knock-in rat lines with Cre recombinase at the dopamine D1 and adenosine 2a receptor loci. In vivo measurement of afferent activity with axon-specific calcium imaging. Modeling the spatiotemporal dynamics of light and heat propagation for in vivo optogenetics. Mesolimbic dopamine signals the value of work. Recombinase-driver rat lines: tools, techniques, and optogenetic application to dopamine-mediated reinforcement. Ultrasensitive fluorescent proteins for imaging neuronal activity. Ultrafast two-photon imaging of a high-gain voltage indicator in awake behaving mice. An optimized fluorescent probe for visualizing glutamate neurotransmission. Distinct temporal integration of noradrenaline signaling by astrocytic second messengers during vigilance. A-77636: a potent and selective dopamine D1 receptor agonist with antiparkinsonian activity in marmosets. Catalytic activation of β-arrestin by GPCRs. An improved BAC transgenic fluorescent reporter line for sensitive and specific identification of striatonigral medium spiny neurons. A variant of yellow fluorescent protein with fast and efficient maturation for cell-biological applications. Crystal structure of the Aequorea victoria green fluorescent protein. Structural basis of spectral shifts in the yellow-emission variants of green fluorescent protein. Imaging striatal dopamine release using a nongenetically encoded near infrared fluorescent catecholamine nanosensor. High-resolution imaging of cellular dopamine efflux using a fluorescent nanosensor array. Sensitive red protein calcium indicators for imaging neural activity. An expanded palette of genetically encoded Ca 2+ indicators. Dissociable dopamine dynamics for learning and motivation.

A neural circuit mechanism for encoding aversive stimuli in the mesolimbic dopamine system. A genetically encoded fluorescent sensor enables rapid and specific detection of dopamine in flies, fish, and mice. Ultrafast neuronal imaging of dopamine dynamics with designed genetically encoded sensors. By enabling multiplexed imaging of dopamine with other circuit components in vivo, RdLight1 opens avenues for understanding many aspects of dopamine biology.
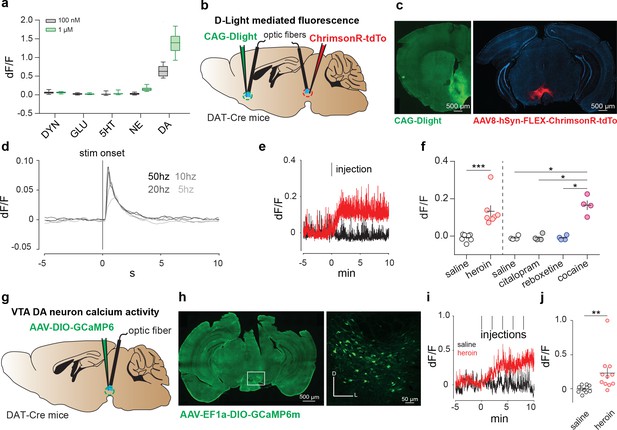
Dual-color photometry revealed that dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens evoked by reward-predictive cues is accompanied by a rapid suppression of glutamate release. We demonstrate the utility of RdLight1 for receptor-specific pharmacological analysis in cell culture, simultaneous assessment of dopamine release and cell-type-specific neuronal activity and simultaneous subsecond monitoring of multiple neurotransmitters in freely behaving rats. RdLight1 can be combined with GFP-based sensors with minimal interference and shows high photostability, permitting prolonged continuous imaging.

We therefore engineered red-shifted variants of dopamine sensors called RdLight1, based on mApple. However, these GFP-based variants cannot be readily combined with commonly used optical sensors and actuators, due to spectral overlap. Genetically encoded dopamine sensors based on green fluorescent protein (GFP) enable high-resolution imaging of dopamine dynamics in behaving animals.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
